Laparoscopic Surgery
Imagine a doctor says – “you have to undergo surgery”, things which strike your mind are pain, ugly scars and the question `When can I return to work?’
No more worries. We are in the era of Laparoscopy (minimally invasive surgery). Laparoscopic surgery has grown to such an extent that the things formerly considered impossible are possible now.

Laparoscopic surgery is also known as “keyhole surgery”, as no large cut is made. This is a mode of surgery, which is performed through small holes created in the abdominal wall. The telescope, which is used to visualise organs inside the body, is passed inside the abdomen via the umbilicus. The abdomen is distended with a gas to make more room. Picture images of the abdominal organs can be viewed on a TV screen. It gives visualization and clarity of the internal organs better than that of conventional surgery since the image is magnified. Two or three small pencil-like instruments are passed on the sides along with it to perform the procedure.
It is virtually painless and cosmetic (skin incision 1 cms or lesser). Your hospital stay is very much reduced so that you can walk home early. Infections and complications are substantially reduced and above all, the trauma of the operation is minimal. There isn’t much restriction in games or sports after surgery.
Initially started in adults to remove gallstones, the technique is now successfully being used for surgeries of other organs in the abdomen like Gall bladder, Stomach, Spleen, Liver, Pancreas, Small and large bowels, Uterus, Kidneys and Major Blood vessels. It is usually done under general anesthesia.
Patients often think that with Laparoscopic surgery, the treatment they are getting is sub optimal when compared to open surgery. That is not true. The surgeon can do a better job utilising the magnified image on the screen.
Lot of studies are there in the world literature favoring Key-hole surgery even for cancer. Studies have shown that your surgeon can remove the abdominal cancer better by Laparoscopic surgery, than by the conventional surgery. In a case of cancer of the liver, Laparoscopic surgery can remove specified part of the liver affected by the disease with minimal blood loss.
Laparoscopic surgery for obesity is an area, which is evolving very fast. You don’t need to exercise a lot; you can reduce your overweight by undergoing a laparoscopic bariatric surgery.
We at Shri Tirupati Hospital have expertise and provide the following surgical procedures:
- Appendicectomy
What is the appendix ?
The appendix is a tube-like organ which is a few centimeters long. It is attached to the beginning of your large intestine, or colon. This is usually below and to the right of your belly button.
You probably know that the appendix can become inflamed. If the appendix needs to be removed, you can live without your appendix and not develop any long term issues.
What is appendectomy ?
This is a type of surgery to remove the appendix. Removal of the appendix cures appendicitis. If appendicitis is untreated, it may rupture or burst open and cause very serious illness or even death
Appendectomy is a common surgery. One way to remove the appendix is by making one larger cut below and to the right of your belly button. This is referred to as an open appendectomy.
Laparoscopic appendectomy removes the appendix using small incisions as shown below.
- Cholecystectomy
What is the gallbladder ?
Your gallbladder is a small organ in your upper abdomen. The abdomen is the area in the middle of your body that holds many organs, including the stomach and gallbladder.
What does the gallbladder do ?
The gallbladder collects and stores a liquid called bile that helps your body break down food. Small, hard deposits called gallstones can form in the gallbladder. This is a common condition. If your gallstones cause health problems, doctors might do surgery to remove it. For example, you might need surgery if your gallbladder is no longer working correctly and you have pain. Your doctor will talk with you about this.
What is cholecystectomy ?
Cholecystectomy is the surgical removal of the gallbladder. Despite the development of non-surgical techniques, it is the most common and effective method for treating symptomatic gallstones. Surgery options include the standard procedure, called laparoscopic cholecystectomy, and an older more invasive procedure, called open cholecystectomy. Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is done using three small 5mm incisions and one 1cm incision as shown below:

- Hernia repair
A hernia is a gap, space or hole in the strong tissue (fascia) that holds muscles in place. Hernias occur if the layers of fascia in your abdomen (belly) become weak. The abdomen is the area in the middle of your body that holds many organs, including your intestines. A gap can form where the fascial layers are weak. Then the inner lining of the abdomen pushes through the gap. It forms a small sac, like a balloon. This is the hernia sac. A loop of intestine or other abdominal tissue can push through the hernia defect (hole) into the hernia sac. You may have discomfort, severe pain, or other problems that could require emergency surgery.
A hernia does not get better over time. It will not go away by itself, and it can get bigger over time. Surgery is the only way to fix a hernia, though not all hernias need to be repaired.
Hernias occur in both men and women, but more frequently in men. There are different types.
3 (a). Inguinal hernia repair
A hernia in the groin area is called an inguinal hernia. Inguinal hernias may be repaired using either open or minimally invasive approaches. Laparoscopy is the ‘Gold Standard’ for bilateral hernia and recurrent hernias. This includes repair of the inguinal area with mesh. The recurrence rate with laparoscopic mesh repair is almost zero percentage. Laparoscopic hernia repair involves three to four small incisions as shown below:

3 (b). Incisional hernia repair
An incisional hernia occurs when the area of weakness through which the hernia occurs, is the result of an incompletely healed surgical wound. These can be the most frustrating and difficult hernias to treat! These hernias present as a bulge or protrusion at or near the area of the prior incision scar. Virtually any prior abdominal operation can subsequently develop an Incisional Hernia at the scar area, including those from large abdominal procedures (intestinal surgery, vascular surgery), to small incisions (Appendectomy, or Laparoscopy). It can be repaired either by conventional open surgery or by Laparoscopic hernia repair. Both the techniques utilise the placement of a mesh.
3 (c). Ventral hernia
A ventral hernia happens in the middle of your abdomen (belly). It can be repaired by conventional open surgery or by laparoscopic surgery.
With tension free ‘mesh’ repair incisional/ ventral hernia can be effectively managed laparoscopically with three small incisions as shown below:

3 (d). Epigastric hernia
An epigastric hernia is a hernia in the epigastric region (upper part of belly) of a human.
3 (e). Umbilical hernia repair
It is a defect at the level of the umbilicus through which the intestines bulge out. With tension free ‘mesh’ repair umbilical/epigastric hernia can be effectively managed laparoscopically with three small incisions as shown below:

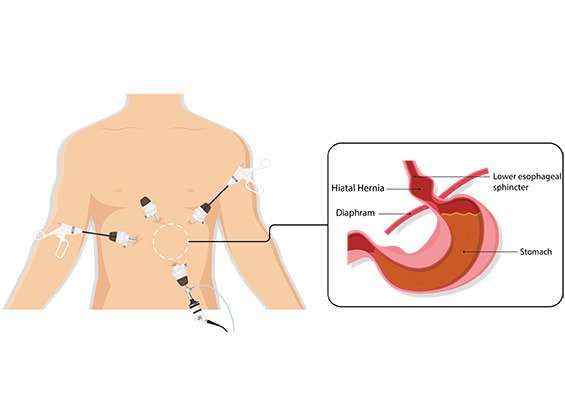
3 (f). Hiatus hernia repair
A hiatus hernia or hiatal hernia is the protrusion (or herniation) of the upper part of the stomach into the thorax through a tear or weakness in the diaphragm. The symptoms include acid reflux, and pain, similar to heartburn, in the chest and upper stomach. The surgical procedure used is called Nissen fundoplication. In fundoplication, the gastric fundus (upper part) of the stomach is wrapped, or plicated, around the inferior part of the esophagus, preventing herniation of the stomach through the hiatus in the diaphragm and the reflux of gastric acid. The procedure is now commonly performed laparoscopically. With proper patient selection, laparoscopic fundoplication has low complication rates and a quick recovery.
Palliative gastro jejunostomy
This procedure is mainly done for patients with stomach cancer causing obstruction of the food path.
Laparoscopic GJ includes either utilization of stapler or hand-sewn method of doing a bypass above the level of obstruction to direct the food to the intestine. This procedure is done only if the stomach cancer is not removable
Intestinal perforation closure (DU / Ileal perforation)
It is an emergency where there occurs a hole in the proximal part of intestine leading to spillage of food particles outside the intestine causing severe pain with collection of pus in the abdominal cavity. This condition requires emergency surgery to save the life of the patient wherein the perforated part is closed and the abdominal cavity is cleaned. Mostly this surgery is performed by an open surgery but in selected cases it can be performed laparoscopically.
Laparoscopic colectomy (Right/ Left/ Hemi/ Total Colectomy)
This procedure routinely performed, mainly for colon cancer. With laparoscopic approach, the size of incision can be minimized and good resection can be achieved. The radicality and extent of the surgery is not compromised while doing a laparoscopic procedure.

Laparoscopic Anterior Resection
This procedure is done for cancer of the rectum. Anterior Resection by conventional method is a complex procedure involving removal of the cancer with adjacent tissues.
Nowadays Laparoscopic Anterior Resection is becoming the Gold Standard for rectal cancer because the procedure does not compromise on removing the whole cancer with adjacent tissues.

Laparoscopic APR (Abdomino Perineal Resection)
This is done for cancer involving the anal canal and sphincter mechanism where the preservation of the natural orifice may jeopardize the longevity of the patient. This surgery involves removing the rectum and anal canal and a permanent stoma is created to divert faeces through the abdomen wall.
Laparoscopic abdominoperineal resection can be done for such type of cancers.
Laparoscopic Rectopexy
This is done for full thickness prolapse of the rectum (rectum coming out of anus). Laparoscopically it is done by dissecting the perirectal area and fixing the rectum upwards.
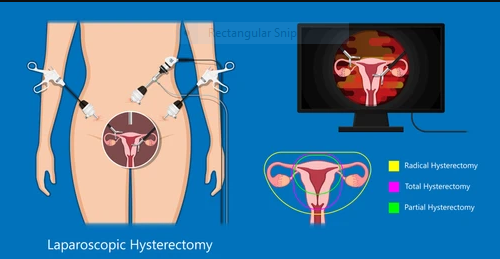
Laparoscopy Assisted vaginal hysterectomy
Laparoscopic Total hysterectomy
A hysterectomy is the surgical removal of the uterus. Hysterectomy may be total or partial. It is the most performed gynaecological surgical procedure. It is done for a number diseases including fibroids, menorrhagia, cancer amongst few other diseases.